A sore throat can be more than just an annoyance; it can signal various underlying health issues. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatments of a sore throat is crucial for effective management and relief. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about sore throats, from their common causes to the best treatment options.
What is a Sore Throat?
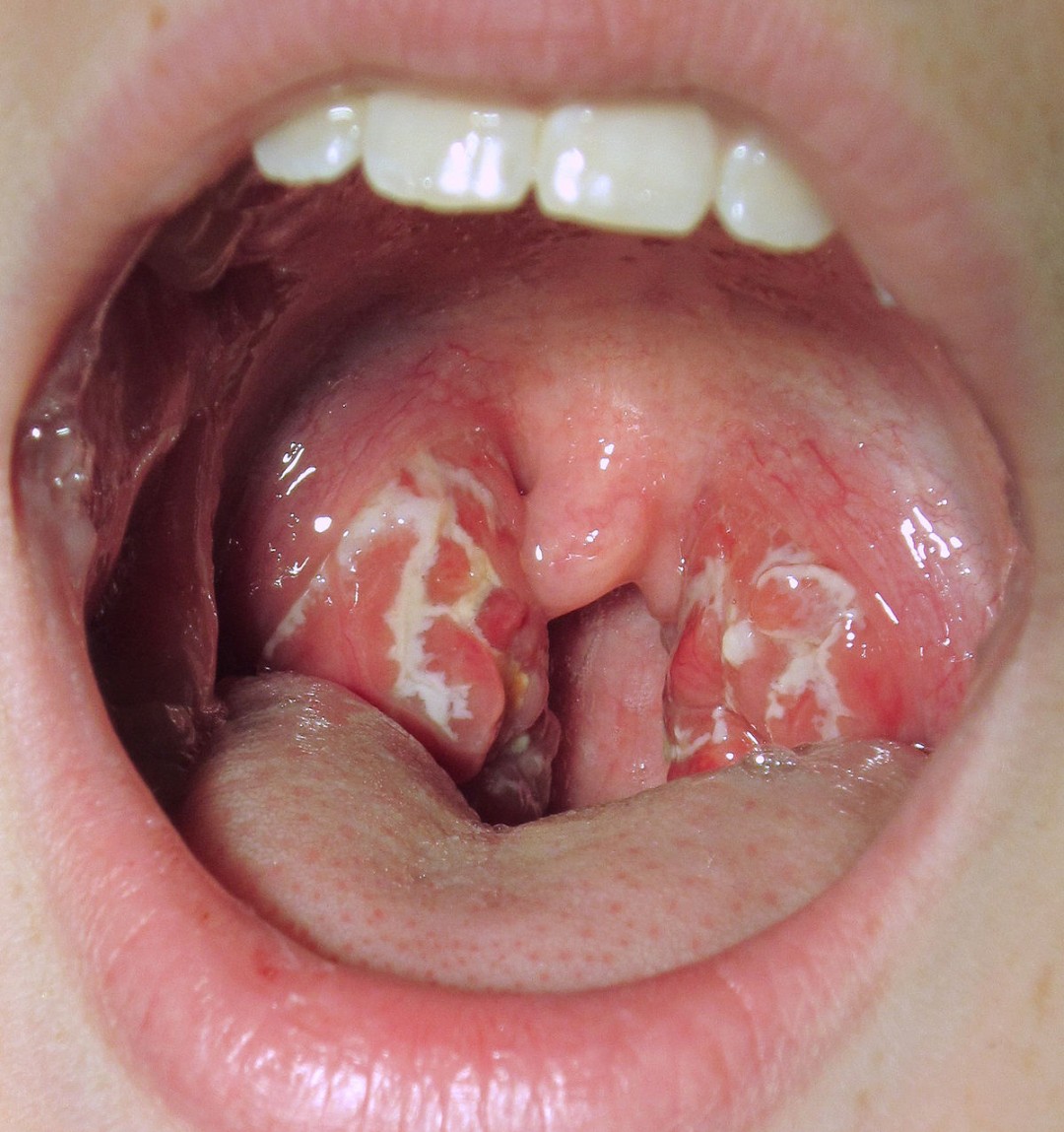
A sore throat, medically known as pharyngitis, refers to pain, irritation, or scratchiness of the throat. This discomfort often increases when swallowing. A sore throat is a common symptom that can result from various factors, including infections, environmental conditions, and lifestyle habits.
Symptoms of a Sore Throat
The symptoms of a sore throat can vary depending on the underlying cause but generally include:
- Pain or a Scratchy Sensation: The most common symptom is pain or a scratchy feeling in the throat.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Swallowing may become painful or difficult.
- Red and Swollen Tonsils: The tonsils may appear red and swollen, sometimes with white patches or pus.
- Hoarse Voice: Changes in voice, such as hoarseness or loss of voice, are common.
- Dry Throat: A dry feeling in the throat, often accompanied by a tickling sensation.
- Swollen Glands: Swelling of the glands in your neck or jaw.
- Coughing: A sore throat is often accompanied by a cough.
Causes of a Sore Throat
Understanding the causes of a sore throat can help in determining the best treatment approach. Common causes include:
Viral Infections:
- Common Cold: The most frequent cause of a sore throat is a viral infection, such as the common cold.
- Influenza: The flu can cause severe sore throat symptoms.
- Mononucleosis: Known as “mono,” this infection can cause a prolonged sore throat.
Bacterial Infections:
- Streptococcus pyogenes (Strep Throat): A bacterial infection that requires antibiotic treatment.
- Tonsillitis: Inflammation of the tonsils, often caused by bacterial or viral infections.
Environmental Factors:
- Dry Air: Dry indoor air, especially in winter, can lead to a dry and sore throat.
- Allergens: Pollen, dust, and pet dander can cause throat irritation and soreness.
- Pollutants and Chemicals: Exposure to tobacco smoke, cleaning products, and other chemicals can irritate the throat.
Lifestyle Factors:
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke can cause chronic throat irritation.
- Overuse of Voice: Yelling, talking loudly, or prolonged speaking can strain the throat muscles.
Diagnosis of a Sore Throat
To diagnose the cause of a sore throat, healthcare providers typically:
- Review Symptoms: Discuss your symptoms and medical history.
- Physical Examination: Examine your throat, ears, and nasal passages.
- Throat Swab: Take a sample from the back of your throat to test for bacterial infections like strep throat.
- Blood Tests: In some cases, blood tests may be needed to rule out conditions like mononucleosis.
Treatment of a Sore Throat
Treatment for a sore throat depends on its cause:
Home Remedies:
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to keep your throat moist.
- Warm Salt Water Gargle: Gargling with warm salt water can reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Humidifiers: Using a humidifier can add moisture to the air, easing throat irritation.
- Throat Lozenges: Lozenges can soothe the throat and provide temporary relief.
- Herbal Teas: Teas with honey, ginger, or licorice can have soothing effects.
Medications:
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can reduce pain and inflammation.
- Antibiotics: If a bacterial infection like strep throat is diagnosed, antibiotics are necessary.
- Decongestants and Antihistamines: These can help if the sore throat is due to allergies or sinus drainage.
Professional Treatments:
- Antibiotics: Prescribed for bacterial infections like strep throat.
- Steroids: In severe cases, corticosteroids may be used to reduce inflammation.
Preventing Sore Throats
Prevention strategies include:
- Good Hygiene: Regular hand washing to avoid infections.
- Avoiding Irritants: Stay away from tobacco smoke and other pollutants.
- Humidifying Air: Use a humidifier to maintain moisture in the air.
- Hydration: Keep your throat moist by drinking plenty of water.
- Avoid Sharing: Don’t share eating utensils, glasses, or food with others to prevent the spread of infections.
Related post: Chlamydia: Symptoms, Treatments, Causes, and More
When to See a Doctor
While many sore throats resolve on their own, seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe Throat Pain: Pain that is severe or persistent.
- Difficulty Breathing: Any trouble breathing or swallowing.
- Joint Pain: Pain that accompanies your sore throat.
- Rash: The presence of a rash.
- High Fever: A fever higher than 101°F (38.3°C).
- Blood in Saliva: Blood in your saliva or phlegm.
- Frequent Recurrences: If you frequently get sore throats.
Conclusion
A sore throat can be a symptom of various conditions, from minor irritations to serious infections. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options can help you manage this common ailment effectively. Maintaining good hygiene, avoiding irritants, and seeking appropriate medical care when necessary are key to preventing and treating sore throats.
Follow our Facebook page for more in-depth Health tips and recommendations